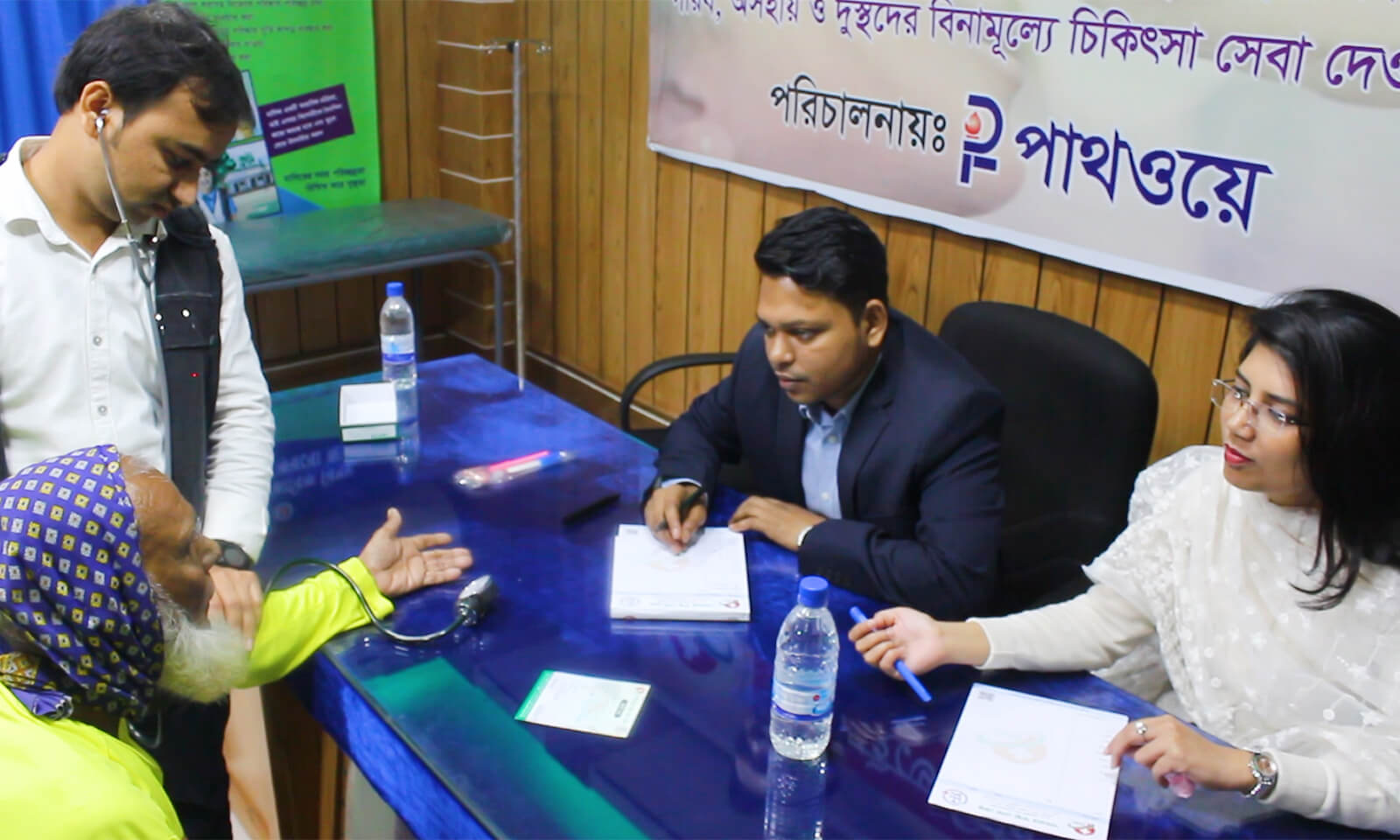
Your doctor may suspect you have diabetes if you have some risk factors for diabetes, or if you have high levels of blood sugar in your urine.
Your blood sugar (also called blood glucose) levels may be high if your pancreas is producing little or no insulin (type 1 diabetes), or if the body is not responding normally to insulin (type 2 diabetes).
Getting diagnosed begins with one of three tests. in most cases, your doctor will want to repeat a test that is high in order to confirm the diagnosis:
- A fasting glucose test is a test of your blood sugar levels taken in the morning before you have eaten. A level of 126 mg/dL or higher may mean that you have diabetes.
- An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) entails drinking a beverage containing glucose and then having your blood glucose levels checked every 30 to 60 minutes for up to 3 hours. If the glucose level is 200 mg/dL or higher at 2 hours, then you might have diabetes.
- The A1c test is a simple blood test that shows your average blood sugar levels for the past 2-3 months. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher may mean you have diabetes.